3 Major Policies
-
1. World Best Education and Care
Consolidating early childhood education and care
As a key national task, the government is committed to improving early childhood education and childcare so that young children in ages 0 to 5 have equal access to quality education and childcare services, regardless of the institution they attend. The Ministry of Education also aims to develop a plan to integrate education and childcare management and narrow down the gap in services. To this end, a regional consolidation of early childhood education and childcare via a new integrated system will be implemented from 2025, ensuring that all children receive the high-quality education and childcare they deserve.
The consolidation of early childhood education and childcare services will also involve expanding relevant subsidies to relieve parents’ burden on educational expenses and to improve the conditions of education and childcare institutions. In addition, the existing childcare gap between kindergartens and daycare centers will be narrowed.
In line with this, a plan to reform the initial teacher education system will be devised. This will enhance teachers’ professionalism and improve their working conditions in newly integrated institutions. Ultimately, these efforts will create an environment where parents can confidently entrust their children to any institutions, guaranteeing “safe and responsible education and childcare from birth.”
Innovating after-school programs through Neulbom (edu-care; quality education and childcare) Schools
Korea has been placing an emphasis on Elementary Childcare Classes as a key policy to create an environment where working parents can raise their children without worrying about childcare, especially as Korea witnesses increasing number of dual-income families and social participation of women.
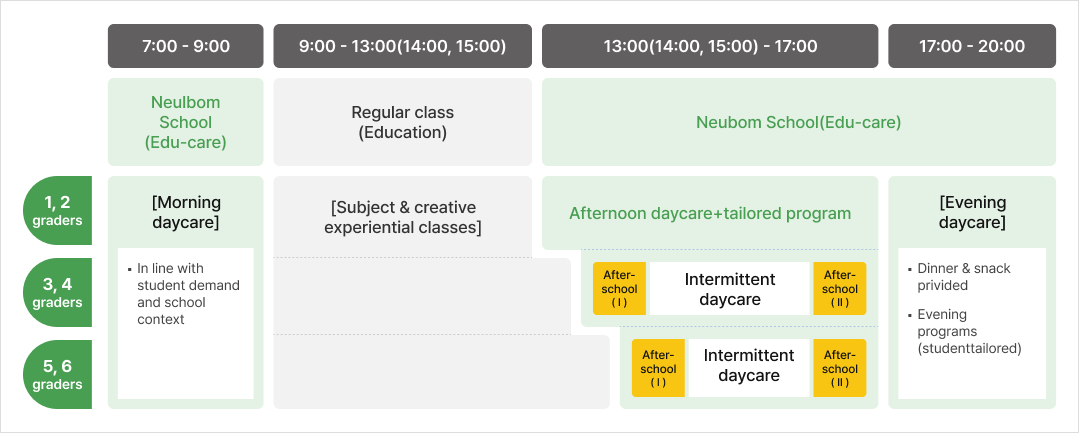
The government announced a new initiative called “Neulbom School.” It is a full-time elementary school education with expanded after-school and childcare classes, highlighting the government’s responsibility over education and childcare. Neulbom School is an integrated edu-care service that utilizes resources both in and outside of the school with an aim to provide quality education and childcare. For lower elementary students, Neulbom Schools not only offer childcare, but they also provide various educational programs on basic academic skills, arts and sports. Neulbom Schools can be used with flexibility, catered to specific demands as needed such as morning, afternoon, and evening childcare.
For upper elementary students, high-quality afterschool programs such as AI and coding classes are offered, along with temporary-basis and/or intermittent childcare. For the first graders of elementary schools, an activity-oriented edu-care program is provided for free at the beginning of the school year for one semester, supporting their smooth transition to school life.
- Neulbom Schools will bring the following changes
- Offering future-oriented/customized after-school programs
- Flexible childcare offered such as Morning/temporary-basis, intermittent / evening (8:00pm) childcare
- Building a dedicated operating system to reduce school workload and strengthening the connection with communities
- Neulbom Schools will bring the following changes
-
2. Global Leading Digital Transformation of Education
Digital Talents and Personalized Learning
The digital education transformation emphasizes the importance of understanding and utilizing digital technologies as a tool and content of education with a growing demand for the systematic digital talent cultivation. To this end, “cultivating one-million-strong digital talents” is a national priority, and the Ministry of Education is pushing for measures to transition to a digital education system that provides individualized education to all students.
In particular, the Ministry of Education has set a vision of “a dynamic innovative growth led by digital talents” to cultivate one-million-strong digital talents by 2026 through the cooperation of the public and the private sectors. To achieve this goal, policies will be initiated to support universities through easing regulations that were preventing higher education institutions to nurture talents and foster leading digital universities, and cultivate manpower of research and development through expanding Brain Korea 21.
In addition, the Ministry of Education will continue its efforts to expand the base of digital talents by increasing the number of class hours on ICT education and launching the Digital Education Sprout Camps.The Ministry of Education is planning to accelerate the educational revolution utilizing AI and edutech, based on the digital foundation-building capacity accumulated over the years. AI-driven courseware (e.g., digital textbooks) will be gradually introduced based on existing paper-based textbooks by 2025.
Courseware is a software designed to deliver effective teaching and learning; teachers can use the learning data analysis results derived from this courseware in their classes, and offer optimized learning tailored to each student’s individual learning goals, capabilities, and pace of learning. -
3. Innovating Higher Education by Breaking Barriers
Redesigning Regional Innovation System and Education (RISE) and Nurturing Glocal Colleges
The Ministry of Education intends to establish the Regional Innovation System & Education (RISE) to foster a regional ecosystem that promotes innovation led by local universities. RISE is a pan-governmental platform with an aim to delegate greater authority to local governments over higher education support, thereby empowering them to facilitate shared growth of the region and higher education institutions.
The government’s goal is to transition the centralized higher education support system, promoting higher education institutions in accordance with the demands of local industries and communities. This, indeed, will bolster higher education institutions as the driving force the regional development. The Ministry of Education will select seven pilot RISE regions to develop a respective model, and proliferate it all across the country in 2025.
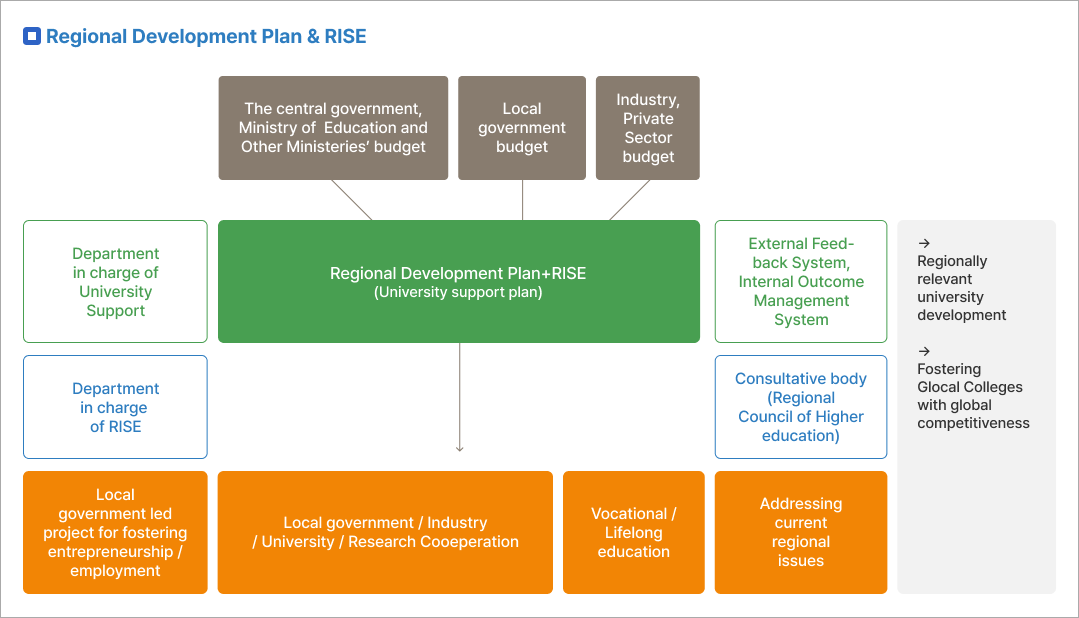
At the same time, the Ministry of Education intends to foster Glocal Colleges to increase the global competitiveness of the nation, regions, and higher education institutions, giving more autonomy to higher education institutions. The Glocal Colleges refer to higher education institutions that break down the barriers between universities and colleges, both within and outside the university as well as between domestic and international entities. The Glocal Colleges will establish partnerships with local communities to drive shared growth between universities and their respective regions. The central and local governments will pursue bold regulatory reforms, and make concentrated investments to Glocal Colleges, while providing special regulatory exceptions to make innovative changes. About 10 Glocal Colleges in non-metropolitan areas will be designated in 2023 and the number will increase to 30 Glocal Colleges by 2026.
In particular, the Ministry of Education intends to provide strong support for local higher education institutions with the stable budget secured by the establishment of “Special Accounting for Higher and Lifelong Education Support,” with education tax as its main source of revenue, from 2023. At the same time, the support for national higher education institutions will be scaled-up to foster local talents and promote a balanced national development, while expanding the scope and size of higher education institutions that share innovation in entrepreneurship education.
Regulatory and structural reforms of HEIs
The Ministry of Education is shifting the direction of policies with an emphasis on autonomy so that higher education institutions can adaptively respond to emerging issues and pursue innovations autonomously. In September of 2022, Higher Education Regulations Reform Council comprised of members from the private sector was formed. It has been tasked with identifying and discussing issues pertinent to reforming regulations on higher education institutions.
In addition, laws are being amended to drastically expand the autonomy of higher education institutions. These amendments aim to eliminate or ease standards that govern the foundation and operation of higher education institutions, such as the creation of new departments, the increase in student quotas, and mergers and closures of higher education institutions. The amendments will also loosen regulations allowing institutions to increase student quotas in leading-edge fields as long as the standard for the number of faculty member is met.
In addition, the Ministry of Education is pushing for measures to abolish the government- led evaluation of higher education institutions. Instead, the results of the accreditation evaluation of the Korean Council for University Education and the financial diagnosis conducted by the Korea Advancing Schools Foundation will be used to begin a full-scale structural reform of higher education institutions that receive financial support from the government.
The Ministry of Education plans to transfer greater authority to local governments to increase the autonomy of regions and schools. This includes the authority to establish or close foreign higher educational institutions in Free Economic Zones. In addition, local governments can promote plans to foster local universities and local talents, working to loosen education-related regulations, such as the establishment of schools and their operation to ensure public education catered to each region. To this end, the government has begun creating laws to designate and operate “Education Autonomous Regions.” This will allow local governments to autonomously design the student selection process and reorganize the curriculum to meet local conditions and receive budget from the central government to support their initiatives.
Source : 2023 Education in Korea

